Title tags were once a simple part of SEO. They helped search engines understand page content and improved click-through rates. Today, their role is broader and deeper. With AI-driven search tools like ChatGPT, Perplexity, and Gemini analyzing and summarizing web content, title tags now help define how AI interprets, classifies, and presents your page in generated answers.
A well-written title tag does more than describe what is on the page. It establishes the topic’s context, clarifies the main entity, and signals to both Google and AI engines what kind of question or intent the page satisfies. The shift from keyword-based ranking to context-based understanding has changed the way we need to think about crafting titles.
Title Tags : Table of Contents
- What is a Title Tag?
- How Titles Evolved: From Keyword Signals to Context Markers
- Why Title Tags Are Critical for Visibility Across Google and AI Search
- What Google Still Looks for in Title Tags
- How AI Engines Interpret Titles Differently
- Anatomy of an AI-Optimized Title Tag
- Writing Framework: Building Titles That Serve Humans and Machines
- Choosing the Right Words and Entities
- Practical Industry Examples
- Common Mistakes and How to Avoid Them
- How to Measure the Effectiveness of Your Titles
- The Future of Title Optimization: From Ranking to Citation
- Conclusion
- Pro Tips for Content Teams in the AI Era
- FAQs
In essence, title tags now serve three audiences: Google crawlers, human readers, and large language models that power AI search experiences. Optimizing for all three requires a nuanced balance between clarity, context, and semantic richness.
A decade ago, this balance was simpler, Google indexed, humans clicked. Now, AI reads, interprets, summarizes, and sometimes even rewrites. Your title tag is the first clue it uses to decide what your content means and whether it’s trustworthy enough to quote.
What is a Title Tag?
A title tag is an HTML element that defines the title of a web page. It appears as the blue, clickable headline in Google’s search results and also shows up at the top of a browser tab when a visitor opens your page. But beyond those familiar uses, the title tag now plays a much larger role, it acts as a semantic label that helps both traditional search engines and AI-powered systems understand the main focus of your content.
In HTML, a title tag looks like this:
<title>Title Tags Explained: How to Optimize Titles for Google and AI Search</title>
For Google, this snippet tells its crawler what the page represents so it can match it to relevant queries. For generative engines like ChatGPT, Perplexity, and Gemini, the same title helps them interpret the topic context, identify entities, and decide whether your page is suitable to reference in an AI-generated summary or answer.
When someone shares your page link on social media or an AI tool fetches content context, the title tag often becomes the primary text shown or cited. It is the first signal that tells both algorithms and readers what your page is really about.
Why Title Tags Are Critical for Visibility Across Google and AI Search
Title tags remain one of the most important signals that define how a page is discovered and understood, not only by Google but also by emerging AI-driven search engines such as ChatGPT, Perplexity, and Gemini. These systems use your title tag to interpret meaning, context, and intent before presenting your page as part of a generative summary or a cited source.
For traditional SEO, the title tag helps search engines determine the relevance of your content to specific queries. It directly influences how your page ranks and how appealing it looks in search results. But in AI search, its role expands. It becomes a semantic entry point, a concise representation of what your content stands for and how confidently AI can reference it in answers.
A strong title tag today must accomplish three goals at once:
- Signal relevance to both Google’s algorithms and AI language models.
- Attract human interest by being clear, specific, and emotionally resonant.
- Build authority and trust by aligning with your brand voice and on-page message.
Together, these factors affect not just your rankings and click-through rate (CTR) on Google, but also your presence in AI-generated answers where citations are often derived directly from page titles.
Google continues to refine how it displays titles in search results. Since 2021, it sometimes rewrites titles that appear unclear or mismatched with page content, often pulling alternatives from headings or anchor text. At the same time, AI systems like ChatGPT or Gemini may paraphrase your title when citing your content, but only if the title communicates intent clearly enough to be recognized.
This makes precision more important than ever. Write titles that naturally match user expectations, describe your content accurately, and use language that is easy for both algorithms and AI models to interpret. Titles that achieve this clarity are less likely to be rewritten or ignored.
If you’re optimizing manually, use a real-time title preview tool like DefiniteSEO to check how your tag appears on Google’s SERP and test its readability and length. The goal is not just balance, it’s alignment: between human curiosity, search engine interpretation, and AI comprehension.
How Titles Evolved: From Keyword Signals to Context Markers
Earlier SEO practices focused mainly on keyword placement and matching search phrases. Title tags that contained exact-match keywords could rank well even if the rest of the content offered little value. This strategy was effective a decade ago when algorithms relied heavily on lexical matching.
Modern search systems, however, understand meaning rather than just words. They evaluate how your title relates to entities, topics, and the intent behind a query. For AI search engines, the title is not just a ranking signal, it is a context marker. It helps the AI model form a semantic representation of your page and determine where it fits within broader topical clusters.
When ChatGPT or Perplexity surfaces a page in an answer, the citation often pulls directly from the title. That means the clarity and structure of your title can affect whether your content is accurately referenced or not.
As natural language models advance, they no longer look for “matching” terms but for understanding. A title like “How to Write Product Descriptions That Convert” signals both purpose and intent. A weaker title such as “Ecommerce Writing Tips” lacks precision and will likely be overlooked.
This transformation demands a mindset shift: titles should no longer be designed around exact-match keywords but around meaningful, well-structured ideas that AI systems can easily interpret and relate to other known entities.
What Google Still Looks for in Title Tags
Despite the rise of AI summarization, Google’s role remains dominant, and title tags still carry significant weight in its ranking system. Google uses them as one of the strongest on-page signals to determine the topical focus of a page.
Google’s guidelines emphasize clarity, brevity, and honesty. Titles should not overpromise or mislead users. They should summarize the page accurately while containing key search phrases that users are likely to query.
Even though AI-generated overviews may reduce direct clicks, Google’s SERP still drives most discoverability. So a good title must appeal to both the algorithm and the searcher’s psychology. It should spark curiosity but also signal relevance instantly.
To achieve this, balance descriptive power with concise structure. Avoid filler words and modifiers. Instead, focus on what makes the page valuable in a single glance.
For example, “How to Optimize Title Tags for AI Search in 2025” works better than “Comprehensive Guide on Title Tag Optimization Techniques for AI and SEO.” The first feels clear and purposeful; the second reads like keyword padding.
How AI Engines Interpret Titles Differently
AI engines approach titles from a perspective of meaning rather than ranking. When large language models analyze a page, they process the title as a summary of intent. Each word contributes to an internal “embedding”, a numerical representation of what the text means. This determines how your content connects to queries and topics.
A strong title helps the model anchor your page within a semantic space. For example, if your title includes the term “Entity Optimization,” AI recognizes it as a specialized concept and links your page to related discussions.
Unlike Google, which judges titles partly through CTR data, AI systems rely on contextual trust. They evaluate how well your title aligns with factual accuracy and topical coherence. If your page title matches known entities and reliable phrasing, your content stands a higher chance of being referenced in AI-generated answers.
Generative systems also value predictive clarity, the title should tell the model what kind of answer it will find. A title like “How to Optimize Blog Titles for AI Search Engines” immediately signals a practical guide, making it easier for AI to quote it in a how-to context.
In practice, this means that vague or overly creative titles may fail in AI search. Clarity now trumps cleverness. The better a title defines a page’s scope, the more confidently AI can interpret and reuse it.
Anatomy of an AI-Optimized Title Tag
Every effective title tag today combines structure, meaning, and readability. To serve both search engines and AI systems, a title should express intent, define a main entity, and provide context.
Key elements of an optimized title include:
- Intent phrase: Signals what the page delivers (for example: “How to”, “Understanding”, “Guide to”, “Comparison of”).
- Main entity: The primary topic or object (for example: “Title Tags”, “Schema Markup”, “EEAT”).
- Context modifier: Adds scope, timeframe, or audience relevance (for example: “for AI Search”, “in 2025”, “for Beginners”).
- Optional brand name: Used at the end for recognition, not at the start.
A clear structure looks like: [Intent Phrase] + [Main Entity] + [Context Modifier]
Examples:
- “How to Write Title Tags That Rank in Google and AI Summaries”
- “Understanding Title Optimization for Generative Search Engines”
- “Crafting SEO Titles for Dual Indexing in Google and ChatGPT”
Titles built with this logic help search engines and AI models understand your page purpose in one glance.
A common mistake is trying to include every possible keyword or modifier. AI systems prefer concise but meaningful phrasing. The ideal title communicates one strong idea instead of several diluted ones.
Writing Framework: Building Titles That Serve Humans and Machines
When creating or revising a title, begin with understanding search intent. Identify what the reader is looking for, then translate that into a clear, descriptive phrase. For traditional SEO, this still means addressing informational, navigational, or transactional intent. For AI systems, it also means making the title semantically complete.
A practical approach:
- Start by identifying the core entity that your page is about.
- Add an action phrase that captures the purpose (learn, guide, compare, improve).
- Add context to clarify your angle or target audience.
- Read it aloud, it should sound natural, not technical.
Example process:
- Topic: Title Tags
- Intent: Guide or Instruction
- Context: AI and SEO in 2025
Final title: “How to Write Title Tags That Work for Both Google and AI Summaries.”
Another effective tactic is using contrast-based phrasing to clarify value, such as “Keywords vs. Entities: How to Write Smarter SEO Titles.” Contrast phrases help both humans and AI see relationships.
Avoid forcing structure. If every title on your site starts with “How to,” it feels formulaic and may even be deprioritized. Mix formats occasionally:
- “The Science Behind SEO Title Optimization”
- “Why AI Search Prefers Clearer Titles”
- “A Practical Framework for Dual-Indexed Title Tags”
Natural variation is not only better for readers but also signals authenticity to AI systems trained to detect over-patterned writing.
Choosing the Right Words and Entities
Selecting the right words is critical. The vocabulary in your title can affect how both humans and AI perceive its relevance. Search engines look for linguistic signals that connect your page to known topics and entities. AI systems rely on the same associations to determine trustworthiness and context.
A few practical guidelines can help:
- Prefer verbs that express value (learn, understand, improve, optimize).
- Include entities that are known concepts (Google, ChatGPT, Gemini, Title Tags, SEO).
- Avoid filler terms like “best” or “top” unless your content supports comparison data.
- Use specific nouns that point to the topic rather than vague descriptors.
- Keep branding minimal, it belongs at the end if used at all.
Titles with clear entities also improve knowledge graph alignment. If AI engines recognize your entities consistently, your content may appear in contextual answer panels or summaries. The goal is to make your title both machine-readable and human-meaningful.
Practical Industry Examples
Different industries require different language tones and structures. A blog post might use curiosity and educational framing, while an eCommerce product page might focus on clarity and trust. Below are examples showing how traditional SEO titles can evolve into AI-optimized ones.
| Industry | Traditional SEO Title | AI-Optimized Title |
|---|---|---|
| Blogging | “Best Blog Title Tips for SEO” | “How to Write Blog Titles That AI Engines Understand” |
| SaaS | “SEO for SaaS Landing Pages” | “Optimizing SaaS Page Titles for Google and AI Search” |
| eCommerce | “Best Product Page SEO Titles” | “How to Write Product Titles That Appear in AI Summaries” |
| Agency | “SEO Title Tag Services” | “Crafting Title Tags That Drive Clicks and AI Citations” |
| Education | “SEO Training Course 2025” | “Learn SEO Title Optimization for AI-Driven Search Engines” |
The difference lies not only in wording but in intention. The AI-optimized titles tell both search engines and humans what the article truly delivers.
Common Mistakes and How to Avoid Them
Even experienced professionals make title tag mistakes that limit visibility or clarity. These often come from legacy SEO habits rather than current best practices.
Common pitfalls include:
- Keyword stuffing: repeating the same phrase to game ranking signals.
- Overuse of modifiers: stacking adjectives (“best, top, ultimate”) that dilute clarity.
- Omitting intent words: titles like “Title Tags 2025” say little about purpose.
- Misplaced branding: adding the brand name first reduces context strength.
- Ambiguous phrasing: unclear or overly broad titles confuse both users and AI.
Avoid these by writing naturally and with purpose. Ask yourself, “Would this make sense if read out loud by someone describing the page?” If not, rewrite for simplicity and flow.
How to Measure the Effectiveness of Your Titles
Optimization does not stop at writing. Measuring title performance is vital. Google Search Console remains the most direct source for traditional metrics like impressions, clicks, and click-through rate.
Beyond those metrics, observe how your titles affect behavioral signals and dwell time on page, bounce rate, and return visits. Titles that promise value but underdeliver can increase bounce rates and signal low satisfaction.
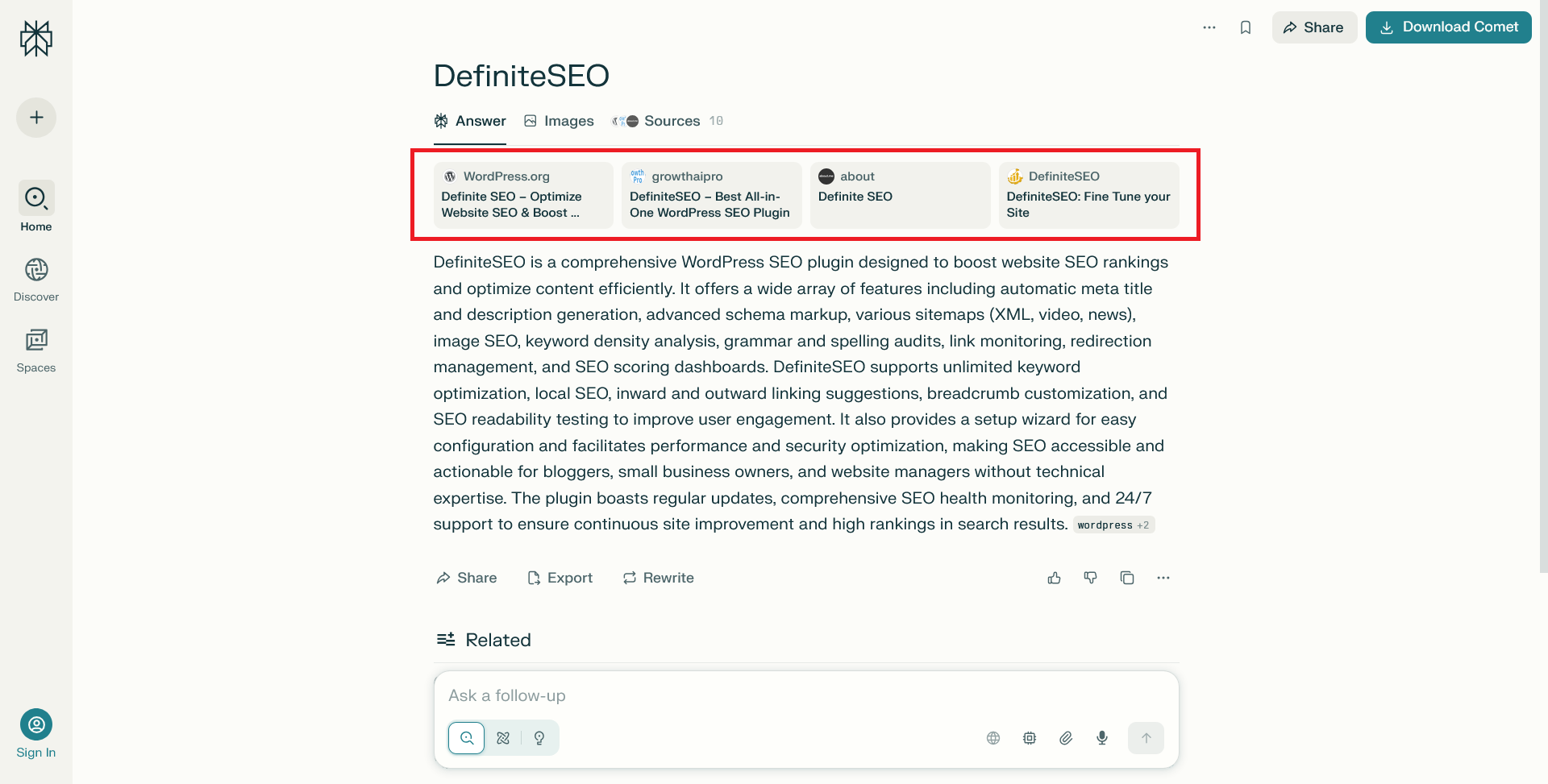
For AI visibility, the evaluation process is different. You can test inclusion in Perplexity, ChatGPT, or Gemini by entering your topic queries and checking for citations or referenced phrases. AI search tools often reference pages with well-structured, credible titles that align closely with the query intent.
A title audit can be performed quarterly. Use the data to categorize your titles into:
- High CTR, High Engagement: Keep as-is.
- High CTR, Low Engagement: Review content alignment.
- Low CTR, High Ranking: Test new titles.
- Low CTR, Low Ranking: Rewrite completely.
Using DefiniteSEO’s Title and Meta Analysis feature helps automate this review, revealing improvement areas for both SEO and AEO perspectives.
Over time, track which titles gain AI citations. That visibility reflects how well your semantic structure aligns with generative engines.
The Future of Title Optimization: From Ranking to Citation
The next phase of title optimization moves beyond rankings. As AI systems integrate more deeply into everyday search behavior, being cited or summarized accurately will become the real metric of visibility.
Titles will act as your first impression for both humans and machines. They will communicate not only what your page is about but how it fits into the broader knowledge ecosystem.
The most effective titles in the coming years will combine three things:
- Precision: a clear main entity.
- Intent clarity: purpose expressed through wording.
- Context: framing within the AI or semantic web environment.
DefiniteSEO’s approach to content and title analysis continues to evolve to support this dual optimization, helping creators stay visible not only in traditional search results but also within AI-generated summaries.
In the long run, title optimization will be less about pleasing algorithms and more about teaching machines how to interpret your meaning correctly.
Conclusion
Writing a title tag is now as much about meaning as it is about marketing. The shift from keyword-matching to semantic understanding means that every word in your title matters. It shapes how Google ranks you, how users click you, and how AI engines interpret you.
As AI search expands, title optimization becomes an intersection of linguistics, clarity, and strategic context. For creators, this means thinking less about “tricks” and more about how clearly they express what their page truly offers.
A well-written title tag remains one of the simplest but most powerful tools to improve both SEO and AEO performance. Done right, it connects your content seamlessly with both human curiosity and machine understanding.
Pro Tips for Content Teams in the AI Era
Crafting titles in the age of AI search is no longer a one-person job. It requires collaboration, clarity, and a shared understanding of how titles influence visibility across both Google and generative engines. Below are some practical, modern-day habits content teams can adopt to keep their workflows efficient and future-ready.
1. Start Every Content Brief with the Title
A strong title sets the direction for the entire piece. It shapes the writer’s approach and helps AI and search engines understand the topic hierarchy from the start.
Before drafting any article, agree on a working title that defines the purpose clearly. Treat the title as a compass for both creativity and optimization, it keeps everyone aligned and reduces later rewrites.
2. Review Titles as a Team
Titles should not be finalized in isolation. A collaborative review between strategists, editors, and SEOs ensures a balance between engagement and semantic accuracy.
Read titles aloud during editorial review. If they sound natural and concise, they’re likely to resonate with both users and AI systems. Collaborative feedback often transforms technically sound but dull titles into phrases that capture intent more effectively.
3. Maintain a Title Variant Library
Having a shared library of proven title formats saves time and ensures diversity. Rotate between structures like:
- “How to [Action] for [Goal or Context]”
- “Why [Concept] Matters for [Audience]”
- “[A] vs [B]: Which Works Better for [Use Case]”
- “The Science Behind [Topic or Outcome]”
This variety helps your content avoid mechanical repetition, signaling freshness and authenticity to AI crawlers that analyze language style consistency across domains.
4. Use Dates and Context Wisely
Adding years to titles can make them appear relevant, but overuse dilutes credibility. Include the year only when trends or guidelines genuinely change over time. Instead, demonstrate timeliness through updated insights and examples within the content itself.
5. Audit and Refresh Older Titles
Every few months, review older posts to ensure their titles still match the content’s focus and the current AI landscape. Replace vague phrasing with intent-driven language and update context words like “SEO” to “AI Search” or “AEO” where appropriate. Small updates can improve both rankings and AI citation potential.
6. Combine Human Creativity with Data Insights
Creative brainstorming remains essential, but back it up with analytics. Study which of your titles attract higher engagement and track patterns in Google Search Console. When titles that perform well share certain traits: clarity, directness, or question framing, document those findings and build your next batch around them.
7. Prioritize Meaning Over Mechanics
Finally, remember that optimization is a byproduct of understanding, not formatting. Write titles that communicate meaning clearly and naturally. AI models favor language that resembles authentic human phrasing. A title that feels helpful, relevant, and precise to a person will almost always perform better across both Google and AI-driven systems.
FAQs
Q1. Should I still include my brand name in the title tag?
Yes, but place it at the end, separated by a pipe or hyphen. This keeps the main topic and intent clear while preserving brand visibility.
Q2. How often should I update my title tags?
Review titles every few months or when updating major site content. Refresh contextual modifiers like the year or focus area to keep them current.
Q3. Do AI engines directly read and rank title tags?
AI engines do not “rank” titles in the same sense as Google, but they interpret titles to understand topic context and relevance for answer generation.
Q4. What makes a title AI-ready?
An AI-ready title clearly expresses intent, includes recognizable entities, and fits naturally into a semantic context. It avoids vague or overly promotional wording.
Q5. Can I test AI citation visibility?
Yes. Search your core topic on Perplexity or ChatGPT and see if your content or domain appears in the generated answers or references.